Feta Cheese and Food Preparation

Feta cheese nutrition facts – Feta cheese, with its tangy, salty flavor and creamy texture, is a remarkably versatile ingredient that can elevate numerous dishes. Its unique characteristics lend themselves to both simple preparations and more complex culinary creations, making it a staple in Mediterranean and global cuisines. Understanding how to best utilize feta in cooking, while minimizing added salt and unhealthy fats, is key to enjoying its nutritional benefits.
The culinary applications of feta cheese are extensive and diverse. Its robust flavor profile complements a wide array of ingredients, from fresh vegetables and fruits to proteins and grains. Knowing how to incorporate it effectively allows for the creation of flavorful and healthy meals.
Culinary Applications of Feta Cheese
Feta’s versatility shines through in its adaptability to various cooking methods and cuisines. It can be used as a primary ingredient, a seasoning, or a finishing touch, depending on the desired outcome. The following list showcases its broad appeal.
- Salads: Feta adds a salty, creamy counterpoint to fresh greens, tomatoes, cucumbers, and olives, forming the base of classic Greek salads or adding a unique twist to other salad combinations.
- Baked Dishes: Incorporating feta into baked goods like spanakopita (spinach pie) or savory tarts contributes a rich, salty flavor and creamy texture.
- Pasta Dishes: Crumbled feta can be tossed with pasta and vegetables for a quick and easy meal, or used as a topping for a more sophisticated presentation.
- Savory Tarts and Quiches: Feta’s distinct flavor profile complements the eggs and crust in these dishes, adding a salty tang that balances the richness.
- Sauces and Dressings: Blended with herbs, lemon juice, and olive oil, feta can create a unique and flavorful sauce or dressing for various dishes.
Incorporating Feta into Healthy Recipes
To maximize the nutritional benefits of feta while minimizing added salt and unhealthy fats, it’s important to focus on preparation methods and complementary ingredients. Choosing low-sodium feta is a crucial first step. Furthermore, pairing it with nutrient-rich vegetables and lean proteins helps create a well-balanced and healthy meal.
Limiting the amount of added salt during preparation is essential. The inherent saltiness of feta should be sufficient in most recipes. Additionally, opting for olive oil over butter or other high-fat cooking oils contributes to a healthier overall dish. Focusing on recipes that emphasize fresh ingredients and minimize processed components further supports a healthier dietary approach.
Examples of Healthy Feta Cheese Recipes, Feta cheese nutrition facts
The following recipes highlight feta’s versatility while prioritizing nutritional value and minimizing added unhealthy fats and sodium.
1. Greek Salad with Grilled Chicken: This vibrant salad features crisp romaine lettuce, juicy tomatoes, ripe cucumbers, Kalamata olives, and grilled chicken breast, all topped with crumbled low-sodium feta cheese and a light lemon-herb vinaigrette. The dish is visually appealing with its contrasting colors and textures: the deep green lettuce, the bright red tomatoes, the dark olives, and the creamy white feta against the light brown grilled chicken.
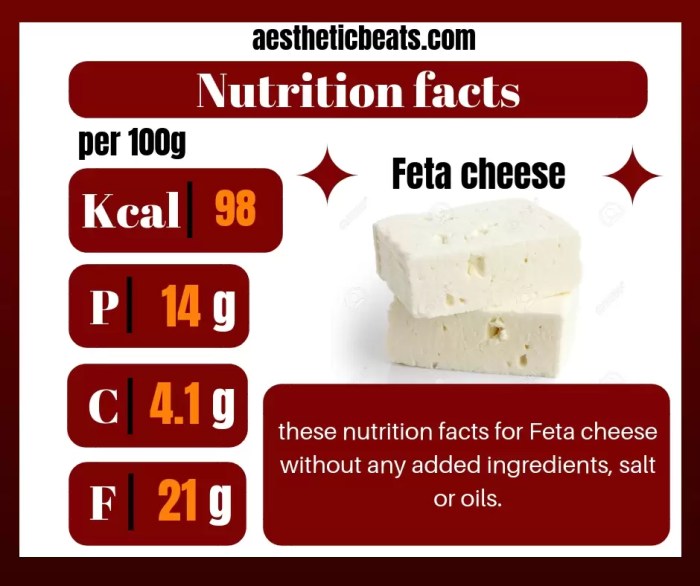
Feta cheese, a staple in Mediterranean cuisine, offers a good source of protein and calcium. However, comparing its nutritional profile to something like a Big Mac reveals a stark contrast; for instance, you can check the big mac nutrition facts to see the difference in fat and sodium content. Returning to feta, it’s important to consume it in moderation due to its relatively high sodium levels.
The aroma is fresh, herbaceous, and slightly tangy from the lemon and feta.
2. Baked Feta and Vegetable Tart: A flaky pastry crust is filled with a mixture of roasted vegetables like zucchini, bell peppers, and onions, all topped with crumbled low-sodium feta cheese and a sprinkle of fresh herbs. The tart’s appearance is rustic and appealing, with the golden-brown crust contrasting with the colorful vegetables and creamy white feta.
The texture is a delightful combination of flaky crust, tender vegetables, and creamy feta. The aroma is warm, savory, and slightly herbaceous, with a hint of the feta’s tanginess.
3. Feta and Spinach Stuffed Chicken Breast: Lean chicken breasts are stuffed with a mixture of sautéed spinach, sun-dried tomatoes, and crumbled low-sodium feta cheese, then baked until cooked through. The stuffed chicken breasts present a visually appealing combination of the pale chicken, vibrant green spinach, and the creamy white feta. The texture is tender and juicy chicken with a slightly creamy, salty filling.
The aroma is savory and herbaceous, with a subtle hint of the feta’s tanginess.
Feta Cheese Production and Sourcing: Feta Cheese Nutrition Facts
Feta cheese production, a process steeped in tradition, varies significantly depending on geographical location and producer practices. Understanding these variations is key to appreciating the diverse flavor profiles and textures found in different feta cheeses. The process generally involves specific milk types, a crucial aging process, and adherence to regional regulations which influence the final product.
Traditional feta cheese production relies heavily on sheep’s milk, often blended with goat’s milk. The exact ratio depends on regional customs and the producer’s preferences. This milk is then pasteurized (or, in some traditional methods, left unpasteurized) before the addition of rennet, an enzyme that coagulates the milk proteins, forming curds. These curds are then cut, drained, and salted, often in brine.
The salting process is crucial, not only for preservation but also for imparting the characteristic salty tang to the final product. The cheese is then aged, typically in brine, for varying periods, impacting its texture and flavor.
Traditional Feta Production Methods and Regional Variations
The quality of feta cheese is profoundly influenced by both the production method and its geographical origin. Traditional methods, often passed down through generations, emphasize the use of unpasteurized milk and longer aging times, resulting in a more complex and intense flavor. Conversely, commercially produced feta often utilizes pasteurized milk and shorter aging periods, leading to a milder, less pungent taste.
Regional variations also contribute to the diversity of feta, with Greek feta, for example, often being known for its firm texture and salty, tangy flavor, while other regional variations may present softer textures and milder tastes.
| Milk Source | Aging Time (minimum) | Flavor Profile | Regional Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100% Sheep’s Milk | 2 months | Sharp, tangy, intensely salty | Certain regions of Greece |
| Sheep’s and Goat’s Milk Blend (70/30) | 1 month | Milder saltiness, creamy texture | Some parts of Bulgaria |
| Pasteurized Sheep’s Milk | 3 weeks | Less intense flavor, softer texture | Many commercially produced varieties |
| Cow’s Milk (less common for traditional feta) | Variable | Generally milder than sheep or goat milk feta | Some less traditional producers |
Question & Answer Hub
Is feta cheese suitable for lactose-intolerant individuals?
Feta cheese contains lactose, although the amount varies depending on the aging process. Some individuals with mild lactose intolerance may tolerate small amounts, while others may experience digestive discomfort. Lactose-free feta options are also available.
How does feta cheese compare to other cheeses in terms of sodium content?
Feta cheese generally has a higher sodium content compared to many other cheeses like cheddar or mozzarella. This is due to the brining process during production. Individuals watching their sodium intake should be mindful of portion sizes.
Can feta cheese be part of a weight-loss diet?
Feta cheese can be included in a weight-loss diet in moderation. Its protein content contributes to satiety, but its fat and calorie content should be considered within overall daily caloric goals. Choosing smaller portions and pairing it with nutrient-dense foods can help manage weight effectively.
What are some creative ways to use feta cheese beyond salads?
Feta’s versatility extends beyond salads. It can be crumbled into baked dishes, used in sauces, incorporated into stuffed vegetables, or added to omelets and frittatas for a burst of salty flavor.