Health Benefits and Risks of Pork Chop Consumption

Pork chops nutrition facts – Pork chops, a popular and versatile cut of meat, offer a good source of protein and various nutrients. However, understanding both the potential benefits and risks associated with their consumption is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section will explore the nutritional advantages and disadvantages of incorporating pork chops into a balanced diet, comparing them to other protein sources.
Understanding pork chop nutrition facts is crucial for balanced eating. When comparing protein sources, it’s helpful to examine alternatives; for instance, you might consider checking out the nutrition facts for flank steak to see how it differs in terms of fat content and overall nutrient profile. Returning to pork chops, remember that portion size significantly impacts the nutritional value.
Protein Content and its Benefits
Pork chops are an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues, including muscle. This protein contributes significantly to satiety, helping you feel full and satisfied after a meal, potentially aiding in weight management. A 3-ounce serving of pork chop provides approximately 25-30 grams of protein, a substantial portion of the daily recommended intake for many adults.
This high protein content makes pork chops a valuable component of diets focused on muscle growth and maintenance, particularly for individuals engaged in regular physical activity.
Risks Associated with High Pork Chop Consumption, Pork chops nutrition facts
While pork chops offer nutritional benefits, excessive consumption can pose health risks. Pork chops, like other red meats, contain a relatively high amount of saturated fat. High saturated fat intake is linked to increased levels of LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol), a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease, including heart disease and stroke. Additionally, processed pork chops, such as those heavily cured or containing added sodium, can contribute to high blood pressure.
Therefore, moderation is key. The American Heart Association recommends limiting saturated fat intake and suggests choosing leaner cuts of pork and preparing them with healthy cooking methods. A recommended serving size is typically 3-4 ounces, equivalent to roughly the size of a deck of cards.
Comparison to Alternative Protein Sources
Choosing a balanced diet involves considering various protein sources. Let’s compare pork chops to chicken breast and fish:
The following table summarizes the advantages and disadvantages of each protein source:
| Protein Source | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Pork Chop | Good source of protein, rich in B vitamins, readily available. | Higher in saturated fat than chicken breast and some fish, can be higher in sodium if processed. |
| Chicken Breast | Lower in saturated fat than pork chops, readily available, versatile. | Can be lower in some nutrients compared to pork chops (e.g., B vitamins). |
| Fish (e.g., Salmon, Tuna) | Excellent source of omega-3 fatty acids, beneficial for heart health, lower in saturated fat than pork chops. | Can be higher in cost than pork chops or chicken, some types contain mercury. |
Pork Chop Preparation and Nutritional Impact: Pork Chops Nutrition Facts
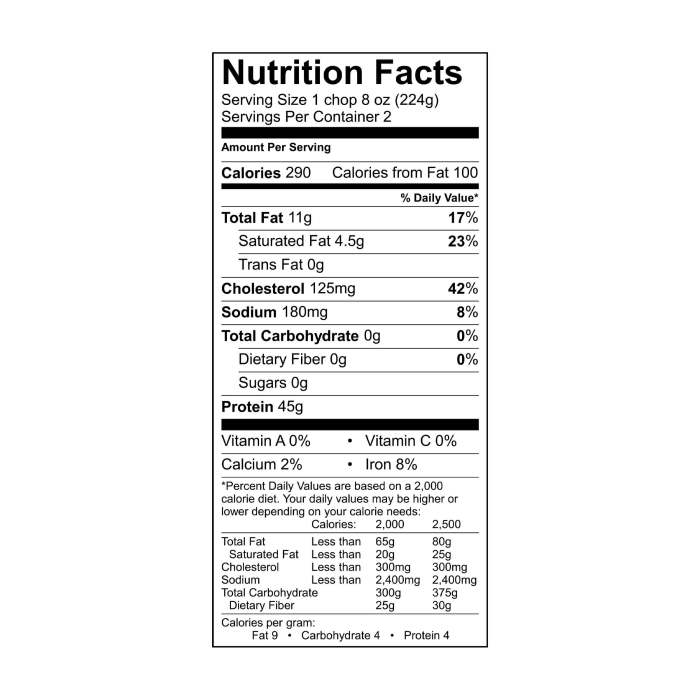
The way you prepare a pork chop significantly impacts its nutritional value. Different cooking methods affect the fat content, nutrient retention, and overall caloric profile. Understanding these changes allows for informed choices regarding healthier cooking techniques.
Cooking methods influence both the fat content and the retention of essential nutrients in pork chops. For instance, methods that involve adding fat, such as frying, increase the overall fat content of the final dish. Conversely, methods that minimize added fats, like grilling or baking, result in a leaner product. The high temperatures associated with some methods can also affect the nutrient profile; some vitamins and minerals might be lost during the cooking process.
Cooking Methods and Nutritional Effects
Several common cooking methods influence the nutritional content of pork chops. Let’s explore some popular choices and their effects.
| Cooking Method | Fat Content | Nutrient Retention | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grilling | Low to moderate (depending on fat trimming) | Generally good; some B vitamins may be lost through dripping juices. | Produces a flavorful chop with visible char marks. Requires careful monitoring to avoid burning. |
| Pan-frying | Moderate to high (depending on oil used and amount) | Moderate; some nutrients may be lost to the oil. | Quick and easy method, but can lead to higher fat content if not done carefully. Using a non-stick pan and minimal oil helps mitigate this. |
| Baking | Low to moderate (depending on added fats) | Good; retains more nutrients compared to frying. | Produces a tender and juicy chop, especially when using a marinade. |
| Broiling | Low to moderate (similar to grilling) | Good to moderate; similar to grilling in nutrient retention. | Fast cooking method that creates a crispy exterior. Requires close supervision to prevent burning. |
Impact of Added Ingredients
Adding ingredients like breading and sauces significantly alters the nutritional profile of pork chops. Breading adds extra carbohydrates and calories, while sauces can contribute to increased fat, sodium, and sugar content. It’s important to consider these additions when aiming for a healthier meal.
| Added Ingredient | Impact on Calories | Impact on Fat | Impact on Sodium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breading (e.g., breadcrumbs) | Increased | Increased | Potentially increased, depending on the breading mix. |
| Creamy Sauces (e.g., Alfredo) | Significantly increased | Significantly increased | Moderately increased |
| Tomato-based Sauces | Moderately increased | Low to moderate increase | Moderately increased, depending on added salt. |
| BBQ Sauce | Moderately increased | Low to moderate increase, depending on the type | Moderately increased, depending on the type |
FAQ Summary
Are pork chops a good source of protein?
Yes, pork chops are an excellent source of high-quality protein, essential for building and repairing tissues.
How many calories are in a pork chop?
The calorie count varies significantly depending on the cut, size, and cooking method. A 3-ounce serving can range from 150 to 300 calories.
Can I eat pork chops if I’m on a low-fat diet?
Choose lean cuts like loin chops and opt for grilling or baking to minimize added fat. Portion control is key.
Are pork chops suitable for people with high cholesterol?
Due to their saturated fat content, individuals with high cholesterol should consume pork chops in moderation and choose lean cuts.
What are some healthy ways to cook pork chops?
Grilling, baking, and pan-frying with minimal added oil are healthier options than deep-frying.



